From time immemorial, migration processes have had a significant impact on the development of our civilization. The impact of migration on the modern world is simply colossal. The multifaceted concept of migration, its conditions, principles and consequences become the object of research by economists, sociologists, demographers... It is also advisable for potential immigrants to navigate the immigration trends that are observed in the modern world.
- 4.1 Video: Europe's migrant crisis
Classification of population migrations
The very concept of “migration” arose a long time ago. The term came to us from the Latin language (Latin migratio - relocation). Migration is the movement of individuals, groups, and sometimes entire peoples between localities, regions of the same state, or even between countries. The versatility of migration is determined by the location of the move, its duration, frequency and many other parameters.
The right of people to change their place of residence and move freely is enshrined in Article 13 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
There are two main types of migration processes. They are:
- internal;
- external.
In the first case, we are talking about the movement of citizens of one state within its borders. This could be the movement of residents of rural areas to cities (the consequence of which is urbanization), as well as residents of one region to another.
Persons who migrate internally are called, accordingly, internal migrants. This is easiest to explain with clear examples.
Residents of the Leningrad region are moving to St. Petersburg. This will be internal migration, in which residents of a small settlement move to a developed regional center. As a second example, we can consider the move of a resident of Irkutsk to Moscow. A citizen of the Russian Federation moves from one region of the country to another. He will also be considered an internal migrant.
External migration clearly means that a migrant leaves his or her country and moves to another state. This can happen for various reasons. Example: a Russian moves to work in Germany. This process will be called external migration, and the hero of our example will be called an external migrant.
Many research institutions around the world are studying migration processes in modern conditions; they are studied by experts in the field of economics and demography. Understanding current trends forms the basis for recommendations to the governments of different countries, influential international organizations, the United Nations on correcting certain areas of migration, making changes to legislation, and so on. The result should be the optimization of the global labor market, internal labor markets in various regions of the planet, as well as in individual states. In addition, expert recommendations help government officials anticipate the development of the demographic situation in their country in the near and distant future, as well as adjust legislative and social policies regarding immigrants.
The issue of shuttle migration should be separately considered. This is the name given to the nature of border crossing by migrants, when they go abroad for a certain time, then return to their homeland, and this happens many times. For example, shuttle labor migrants are Russians who work in EU countries for several months, subsequently return home, and then go back to Europe to work.
Migrants have become a big problem for modern Europe
Types of population migration
All migrations can be divided into two main types: internal and external.
Internal migration is the movement and further placement of the population within one state. The main internal migrations include:
- Migration of people from rural to urban areas is typical for all countries of the world and is associated with the increasing urbanization of regions.
- Migration to new, poorly developed areas of the country. Thus, residents of Sweden, Finland and Norway are moving to live in Lapland, residents of the United States are going to conquer Alaska, the Chinese are developing the western lands of China, and in Brazil the Amazon continues to be a little-developed territory.
Rice. 2. Amazon.
- Seasonal migrations are associated with seasonal work or recreation.
- Commuting migrations – border crossings occur daily and are associated with work or study in another state. In border areas, this type of movement is commonplace.
External migration is the movement of population from one state to another. They come in several types:
- Intercontinental - movement of population from one continent to another. These include migrations of people from European countries to Australia and America.
- Intracontinental - the movement of people from one country to another, while both countries are located within the same continent. For example, Mexicans are trying to move to permanent residence in the United States, residents of Eastern European countries are migrating to Western European countries.
Recently, a special form of migration called “brain drain” has been gaining momentum. It points to the movement of scientists, qualified specialists and cultural figures from developed countries to developing ones.
Migration Dimensions
Migration processes in the modern world practically never stop. Migration can be individual, limited or mass. In this case, everything depends on how systematically the move from one place of residence to another is carried out, regardless of whether it is internal or external migration, as well as on how many people take part in this process.
For example, a resident of one of the regional centers of the Novosibirsk region moves to the regional center. This will be an individual migration. Even if he moves to another country, the quantitative definition of migration in this case will not change. The movement of Ukrainian residents to work in Poland, which has become widespread, will accordingly be considered mass migration. The concept of limited migration can be considered situationally and is an intermediate link between individual and mass migration. This could be the relocation of residents of one locality to another or the relocation of representatives of one profession to work in another country. It all depends on the context in which the concept of migration is considered in this case.
Modern scientific theories that explain the reasons for the settlement of humanity across different continents of the planet, different regions and different countries, attach great importance to migration. At one time, thanks to the mass migration of the population of the Old World to the New World, the United States of America, Canada, Mexico, the countries of Central and Latin America, Australia and New Zealand appeared on the political map of the world. These countries were essentially created by immigrants. In the Russian Empire, population migration actually made it possible to develop the expanses of Siberia and the Far East and to populate lands in the Far North.
Impact of migration on population structure
Definition 1
Population migration is a complex social process that affects almost all aspects of the economic, social and cultural life of peoples. The structure of the country's population is formed under the influence of natural movement and under the influence of migration processes.
As a result of population migration, the following changes in demographic processes are observed:
- the gender and age structure of the population is changing;
- the ethnic composition is disrupted;
- social composition changes;
- in areas with population outflow exceeding replacement, the birth rate decreases and the proportion of the elderly population increases;
- in areas with an influx of migrants, the proportion of young people is growing, and the rate of reproduction is increasing;
- the quantity and quality of labor resources changes.
Help with student work on the topic The impact of migration on the population
Coursework 420 ₽ Essay 280 ₽ Test paper 250 ₽
Get completed work or consultation with a specialist on your educational project Find out the cost
Demographic dynamics are predetermined by the following components: fertility, mortality, migration. Each component influences the formation of the age structure.
Note 1
One of the goals of the concept of replacement migration, developed by the UN in the 90s. XX century – counteracting demographic aging. Replacement migration occurs where natural population reproduction is insufficient to replace generations. Migration compensates for the “natural” population decline and mitigates the consequences of its aging, compensating for the reduction in the working-age share of the population. Migration policies lead to faster results than measures in the field of fertility and mortality.
Attracting migrants increases the working-age population. However, some migrants are of pre-retirement age or elderly, which subsequently leads to an aging population.
The composition of migrants affects the educational and cultural level of the population. Thus, the relocation of residents from the city to rural areas or areas remote from civilization contributes to the formation of a higher level of professional qualifications and culture among the local population; on the contrary, the influx of the rural population into cities has the opposite effect.
Are you an expert in this subject area? We invite you to become the author of the Directory Working Conditions
The influx of migrants of reproductive age is contributing to a change in demographic trends. As a rule, the birth rate among migrants is higher than that of the local population, which leads to an increase in ethnocultural diversity. With the outflow of part of the indigenous population, this can lead to serious problems in the state.
Reasons for migration
There can be many reasons for migration. Much depends on the life circumstances of an individual person or an individual family, as well as on the developing political or economic situation in a particular state or its region. We can consider the reasons for migration both for an individual person and for representatives of certain nationalities or religious denominations, for representatives of certain professions, and so on.
Video: examples of migration processes
Economic factors of migration
The main incentives for migrants in peacetime are economic. People always strive to find an opportunity to earn more, improve their financial situation, purchase their own home and, ultimately, achieve professional self-realization.
Some people are ready for global changes, while others are not. That is why not all representatives of the population take part in the migration process.
The main incentives for migrants in peacetime are economic.
Family motives
Many people leave their homes and move to other cities, regions or even countries when reuniting with families, when they are invited by close relatives, for example, children or parents, brothers or sisters. Marriage unions also contribute to family migration. For example, a resident of Omsk marries a resident of Vladivostok and, naturally, moves to her husband’s homeland. In this case we are also talking about family migration. Along with economic reasons, family reasons are one of the determining factors in modern migration processes.
Forced migration
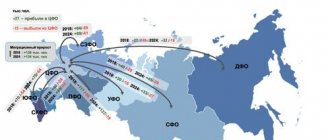
People who leave their native land due to armed conflicts, famine, epidemics and other force majeure circumstances are forced migrants. And their move to other countries or regions is called forced migration. In the modern world, forced migration, unfortunately, remains a relevant phenomenon. For example, everyone knows about the migration crisis in Europe. Armed conflicts and wars in the countries of the Middle East, famine in North-East Africa, as well as the desire of residents of the entire African continent to improve their financial situation by working in highly developed European countries have led to the fact that it has become very difficult for the European Union to control migration traffic. This, in turn, caused an internal political crisis in many European Union member countries, as a result of which representatives of the radical political wing began to come to power. In many ways, the proposed withdrawal of Great Britain from this interstate formation was justified precisely by the migration crisis in old Europe. By the way, the current US President Donald Trump won the election largely thanks to promises to tighten the United States policy towards forced migrants.
People who leave their native land due to armed conflicts, famine, epidemics and other force majeure circumstances are forced migrants
I quite often encounter situations where people cannot clearly distinguish between the concepts of migration, immigration and emigration. Therefore, I will try to clarify this issue. The easiest way to explain the difference in terminology is with examples. Let's consider moving a citizen of the Russian Federation to Germany. His departure from his homeland will be called emigration, and his compatriots will consider him as an emigrant. Arrival on German soil will, in turn, be called immigration. For native Germans, a Russian who moves will be an immigrant. But, for example, for residents of neighboring Austria, who are in no way affected by the process of a Russian moving to Germany, he will be considered just an ordinary migrant. And his move from Russia to Germany will, accordingly, simply be migration. Incorrect use of these terms can often lead to a distortion of meaning.
A few words should also be said about existential migration. It means the movement of migrants to other countries to understand the essence of existence, the desire to understand some of its aspects. In particular, domestic yogis move to India or Nepal in order to learn spiritual truths and strive to follow a certain path prescribed by their religious teachings.
Reasons for population migration
Many people see the opportunity for a better life abroad – new, attractive prospects for work or study. Higher wages and career opportunities attract people who want to achieve economic stability.
One of the common reasons for population migration is also the tense situation at home: political unrest, strikes, military actions, anti-terrorist operations.
People may leave their country due to climatic conditions unsuitable for normal life. These include frequent natural disasters and other natural anomalies, due to which the quality of life is significantly deteriorated.
Rice. 3. Volcanic eruption.
With any manifestations of migration, each state tries to combat its consequences. As the flow of migrants increases, the government takes control of the number of jobs and wages and provides all possible financial assistance. If, on the contrary, there is an outflow of population from the country, the state pursues a demographic policy designed for the natural increase of local residents.
Temporary signs of migration
Migration processes also differ in time. Migration can be:
- temporal;
- constant.
In this case, there is no need to go into details, since it is clear that temporary migration means moving for a limited time. For example, a resident of the Krasnodar Territory who moved to Moscow due to a change of job, but intends to return to the Krasnodar Territory after a certain time, will carry out temporary migration. But in the case when he moves to Moscow, purchases housing, and is legalized in the Russian capital, he becomes a permanent migrant, and the process of his move from Krasnodar to Moscow is final and will be called permanent migration. The same statement is true for those who have moved to other countries. But in this case, an additional factor will be obtaining immigration status, through the prism of which (including) the migrant should be considered as temporary or permanent.
Video: Europe's migrant crisis
https://youtube.com/watch?v=9KPPLHLD-kU
Forms of implementation
Migration processes can be organized or unorganized (chaotic). In this case, the division is also very conditional. For example, mass migration during the settlement of the American continent by Europeans was chaotic and could in no way be considered organized. But the resettlement of German colonists to the Russian Volga region, organized by the government of the Russian Empire, was, accordingly, of an organized nature. Organized migration is the movement of individual migrants or their groups (large and small), when the process of moving is regulated by certain migration programs operating in their receiving countries (in many cases, in agreement with the governments of the migrants’ countries of residence).
Migration can also be voluntary or forced. For the first time, the problem of forced migration began to be officially considered at the international level after the Second World War. Post-war Europe saw a process of migration of huge masses of the population, caused by the consequences of this bloodiest of wars in history. For example, the number of forcibly displaced persons, according to experts, included more than 12 million people. The need to coordinate migration processes led in 1951 to the creation of the International Organization for Migration. Over the years of its activity, this structure has become the main international body dealing with migration issues.
Migration concept
Definition 1
Migration is the process of changing permanent place of residence, relocation, movement of people or social groups to another region, geographic area or country for a period of at least six months.
Migration is also understood as one of the forms of population movement, in which a change in place of residence for a significant time and distance is accompanied by significant social, economic, political, demographic consequences (explicit and hidden, positive and negative, current and long-term, etc.).
Migration processes are based on reasons of various natures: political, economic, national, social, religious, etc.
Migrants are persons who voluntarily or involuntarily change their previous territoriality. They are largely subject to marginalization due to the loss of their “territorial roots.” Attachment to a specific place of life greatly affects a person’s mental and somatic health, the sense of ownership, his ethics, the sense of internal space, and the perception of nature. All this gives rise to problems of family, procreation, and ethnicity.
Finished works on a similar topic
Course work Population migration and its types 400 ₽ Abstract Population migration and its types 220 ₽ Test paper Population migration and its types 210 ₽
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
Migration processes can be forced or natural.
The migration process is closely related to mobility (horizontal and vertical), since any migrating individual, in addition to joining a new social group, wants to find better political, economic or social conditions. Population migration is spatial mobility.
In migration processes, intra-settlement and inter-settlement movements are distinguished. In the classical understanding of migration, it includes inter-settlement movements, since they change the picture of population distribution in the region, country, and world.
Definition 2
Inter-settlement movement is a set of inter-settlement movements, i.e. territorial movements of individuals or social groups between settlements, regions, countries, of any duration, not related to or related to work activities.
Depending on the regularity and duration, intersettlement movement has irrevocable (population migration itself) and return (other types of migration) forms.
Do you need proofreading or review of academic work? Ask a question to the teacher and get an answer in 15 minutes! Ask a Question
Legal status
According to its legal status, migration can be legal or illegal. The first assumes that migrants move to other countries on the basis of entry documents, obtain immigration status there, and end up legally present in the territory of those states. This category of migrants is submitted to the statistical records of immigration authorities, and the process itself is largely regulated by the state. An example of state regulation of migration processes can be the introduction of quotas in many countries of the European Union regarding the admission of migrants, as well as the creation of special immigration programs designed to attract certain categories of foreign citizens to the country.
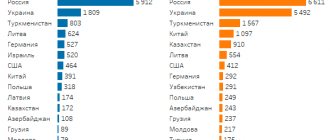
Illegal migration is a huge problem for economically developed countries. According to experts, in the United States of America alone there will be more than 10 million illegal migrants in 2021. The legislation against illegal immigrants is constantly being tightened, the police are fighting against them, but the number of illegal immigrants in the world continues to grow.
In particular, foreigners who arrive in a certain state are considered illegal migrants:
- with false documents;
- by illegally crossing the state border;
- remains on the territory of the country after the period of permits limiting the period of his stay in this state has expired.
All illegal migrants are, to one degree or another, a threat to the society and economy of the host country. This leads to an increase in social tension in its society, an increase in the unemployment rate among the local working population, the creation of chaos in the domestic labor market, as well as the outflow of funds abroad.
Americans are trying to protect themselves from Mexican illegal migrants with a huge wall
Work migration
The main reasons for labor migration are economic. With the current uneven development of states, there is an outflow of labor from depressed regions of the world to more developed ones. People strive to move to places where they can find high-paying jobs with comfortable working conditions and achieve professional self-realization. Experts believe that the share of labor migrants in the total number in the world will constantly grow both in the near and long term. For example, in the United Arab Emirates, immigrants (the lion's share of which are migrant workers) make up 95% of the total population.
People tend to move to places where they can find high-paying jobs with comfortable working conditions and achieve professional self-realization
Migration mechanisms
People are forced to change their usual place of residence as a result of certain conditions:
- Pushing out. Occurs when the living conditions of an individual in his native place become difficult or unsatisfactory. The expulsion of large groups of people is associated with economic crises, severe social upheavals (wars, dictatorships, ethnic conflicts), natural disasters (floods, earthquakes, etc.). The pushing force for individual migration can be the death of relatives, career failures, loneliness, etc.
- Attraction. It is characterized by a complex of attractive conditions and features for living in other places (higher wages, greater political stability, the opportunity to obtain a higher social status). The greater the difference in the economic, social and political conditions of life in the two territories, the more likely the processes of migration to areas with better living conditions are. Attraction can be created artificially to attract “mind” and labor.
- Migration routes. Directly characterize the movement of a migrant from one place to another. Includes the accessibility of the migrant, his family, and belongings to another region; absence or presence of barriers along the way; information to help overcome financial difficulties.
Need advice on your academic work? Ask a question to the teacher and get an answer in 15 minutes! Ask a Question