Migration concept
Definition 1
Migration is the movement of people from one region or state to another.
When moving, people can cross the internal boundaries of administrative entities or travel outside their country. The purpose of moving may be to find a job, study, or start a family. Migration has been characteristic of humanity since ancient times. The population gradually increased, which required the development of new territories. Since the end of World War II, there has been a trend of movement from developing countries to developed countries. Initially, Western European citizens returned from the colonies, followed by indigenous people.
All people who move are called migrants. Migration can be:
Finished works on a similar topic
- Course work Migration in Russia: structure and directions of migration flows 400 rub.
- Abstract Migration in Russia: structure and directions of migration flows 280 rub.
- Test work Migration in Russia: structure and directions of migration flows 210 rub.
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
- internal – between regions, rural settlements and cities,
- external - between countries and continents.
If persons come to the state, then for it they are immigrants. If they leave their homeland, they are considered emigrants.
Most often, migrations are carried out over short distances. Regional centers are attractive. Each migration flow is characterized by its own counter flow. The increase in the population of large cities is associated with population migration, and not with natural growth. Factors stimulating migration are called:
- Industrial development.
- Growth of trade turnover.
- Strengthening transport infrastructure.
Note 1
Thanks to migration, there is a mixing of people living in different countries and even on different continents. There is also a redistribution of labor and production factors. People get the opportunity to find better-paid jobs and create comfortable living conditions for themselves and their families.
Looking for ideas for study work on this subject? Ask a question to the teacher and get an answer in 15 minutes! Ask a Question
The essence of external migrations
Definition 1
International migration is the movement of population across state borders.
The term “migration” itself is of Latin origin and is translated as the movement of people from one region to another for permanent or temporary residence. This phenomenon is studied by various specialists - demographers, sociologists, economists, psychologists.
The number of migrants is growing every year, acquiring global proportions. International migrations have two components – emigration and immigration.
Note 1
Emigration is leaving the country for permanent residence, and immigration is entering the country for permanent residence.
Help with student work on the topic Modern international migrations
Coursework 400 ₽ Essay 250 ₽ Test paper 230 ₽
Get completed work or consultation with a specialist on your educational project Find out the cost
There are several categories of international migrants:
- immigrants admitted to the country legally;
- contract migrants, of whom there were more than 25 million people in the world by the end of the 90s;
- illegal immigrants crossing the border illegally;
- persons seeking asylum for political reasons or due to the difficult economic situation in their country.
The number of international migrants in the world in 2021 reached 281 million people, and in 2000 there were 173 million.
The number of international migrants is growing very quickly, but in 2020 the number of international migrants was reduced by the coronavirus pandemic. Preliminary estimates show that as a result of the pandemic, the number of migrants decreased by about two million.
In absolute terms, a significant increase in the number of international migrants was observed in the last five years, from 2015 to 2021, amounting to 32.6 million people. As for internally displaced persons, between 2000 and 2021 their number doubled from 17 to 34 million people. Forced displacement is caused by political and religious persecution and conflict.
Are you an expert in this subject area? We invite you to become the author of the Directory Working Conditions
Migration has an impact on the demographic situation, and therefore is an important component of the demographic process. They help reduce “demographic pressure” in some cases, and in others they compensate for natural population losses. In addition, migration can lead to changes in the gender and age structure of the population of the receiving country, and in this regard, migration policy is an important component of demographic policy.
As a result of migration, population redistribution occurs both within the country and between states, so it can be considered as an integral part of international politics. International migrations are caused by economic and political reasons. Migration for economic reasons is more or less permanent and involves a huge number of people in the migration process.
Migration in Russia and its structure
Migration in Russia covers both flows - into and out of the country. Internal migration in Russia is slower than external migration. This was facilitated by the program for the return of compatriots, thanks to which more than 150 thousand people returned to the country. In Russian We have already completed a test
Education in Russia in more detail, legislation does not divide migrants into immigrants and labor migrants. Legal migrants are considered foreign citizens who have received a residence permit or a temporary residence permit for a period of 9 months or more, as well as people who have moved to the territory of the Russian Federation and received citizenship.
A large share of movements occurs among labor migrants. Today the number of immigrants exceeds the number of emigrants several times. The main flow of labor migrants to Russia comes from the following countries:
- Uzbekistan.
- Ukraine.
- Kazakhstan.
- Tajikistan.
- Armenia.
- Kyrgyzstan.
- Moldova.
- Azerbaijan.
- Belarus On this topic, we have already completed essay
in more detail. - China.
- Georgia.
- Turkmenistan.
- Germany, Latvia, USA and Lithuania.
In 2021, more than 360 thousand people received Russian citizenship. About 92 thousand people went through the voluntary resettlement program. Invitations to foreign citizens were issued in the amount of 436 thousand. More than 16 million people were registered for migration. About 100 thousand foreign citizens received work permits. About 200 thousand people received temporary residence permits, 151 thousand people received residence permits, and about 200 thousand people received a ban on entry into Russia. All indicators are lower than for the same period in 2021.
There have also been changes in internal migration. Statistical studies have shown that about a third of Russians will soon begin to move from cities to the suburbs. This is due to the emergence of the opportunity to work outside the office (“remotely”).
Directions and types of migration in Russia - briefly
Active migration, periodic or permanent, complex social process of population movement is one of the important socio-economic phenomena. It is both mass and individual. The majority of people changing their place of residence are of working age. Relocation and mobility of the population is considered a normal phenomenon in society.
Consequences of migration
The migration flow affects not only the distribution of labor resources, but
and on the cultural and social component of human life.
The practical phenomenon of population mobility has both positive and negative effects.
- Negative phenomena of excess migration can be:
- demographic failures;
- disproportionate age ratios between the younger and older generations;
- a large discrepancy by gender, when there is an increase in residents of the same sex;
- outflow of labor;
- increasing the load on state social facilities: schools, hospitals, preschool institutions; The positive aspects of internal migration include: stimulating the creation of new jobs;
- replenishment of the region with qualified personnel and labor potential;
- changes in population structure;
- development of small private business.
Distribution of migration within the country
Internal migration movements of the population in the regions of Russia proceed according to the type of movement:
- from a small settlement (village, village) to a city;
- from city to city;
- from the city to small settlements;
- migration between villages and villages.
Migration may be temporary in nature relative to the duration of stay in another territory:
- moving to a permanent place of residence with a low probability of returning to the previous place of stay;
- seasonal movement of the working-age population for temporary employment or study;
- periodic or permanent territorial movements - regular trips to work in nearby large populated areas;
- episodic, tourist, business, pilgrimage, one-time trips are not systematic and occur unevenly throughout the year.
According to the formation of organization, moves are spontaneous, emergency or a pre-prepared process of movement.
The movement of the population is characterized by different parameters:
- the number of citizens arriving and leaving a given locality over a certain period of time;
- the quantitative component of natural population growth and decline;
- geographical migration;
- education of mixed families;
- degree of survival;
- specifics of placement on the territory of the Russian Federation;
- direction of migration flows;
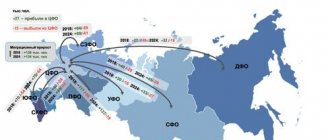
The internal migration flow is a unique phenomenon: residents of northern latitudes move to the southern part of Russia, the population of the Far Eastern Federal District turns out to be a human donor, the Central region attracts the largest number of migrants. The receiving central and southern regions are less susceptible to crisis phenomena, which contributes to the rapid settlement and adaptation of migrants.
Over the past decades, an intense migration flow to various regions has been noticeable in Russia; this is due to social changes that have changed the political and social situation.
Structure of the migration process
Population migration is a complex socio-demographic process, including the following stages:
- preparatory, or initial stage - territorial mobility of the population is formed;
- the main stage is the actual resettlement;
- the final stage is the adaptation of migrants to a new place.
All stages are closely interconnected. So a migrant is a new settler during the period of moving from one territory to another, and a new settler is a former migrant during the period of adaptation and settlement in the area of settlement. New settlers are potential migrants, as they have increased migration activity.
The population living in settlements of different social status, in different regions of the country, differs in the degree of migration mobility, depending on: the level of socialization of individuals, population groups and the entire society of a particular territory; features of the population structure (gender, age, ethnic, genetic, social, etc.).
Finished works on a similar topic
Coursework The structure of population migration 460 ₽ Essay The structure of population migration 260 ₽ Test work The structure of population migration 220 ₽
Get completed work or advice from a specialist on your educational project Find out the cost
Increasing the process of transition of new settlers into the quality of old residents is the antithesis of the intensification of migration mobility of the population. Accommodation characterizes the transition of a migrant to a new settler and a new settler to an old resident.
Survival in a structural sense includes adaptation, the process of adapting to new living conditions at the place of settlement. The survival time of migrants varies and on average is about 10 years.
Survival rate is characterized by wide territorial diversity and depends on
- geographical structure of migration connections;
- migrant exit points;
- relocation area;
- different structure of migrants and population;
- change of settled status during relocation;
- conditions of development in new places
- differences in natural and climatic environments;
- structures of migration flows, etc.
By timely creating conditions for the rapid adaptation of migrants and regulating migration flows, the efficiency of both migration processes and survival can be significantly increased.