Taxation in Russia is a rather interesting system, which is full of interesting features and secrets, both from the legislative side and from the side of practical payments. It is also important to note the presence of a large number of tax regimes for all tastes and colors. One of them is personal income tax, which is very widespread because it applies to almost all citizens of the state. Since its (personal income tax) changes in 2018-2019 were quite important and serious, so it’s really worth considering them and finding out what awaits us in the near future in the country.
Taxes
The entire amount of tax payments that the state collects from the population goes primarily to the benefit of the state budget, as the main source of its financing. This is practically the most important instrument of fiscal policy of the Russian Federation. However, now very often there are bad rumors about upcoming changes, which is quite suspicious and frightens people who are not familiar with it.
Of course, in the current conditions of state education in Russia, you can expect anything. The latest news about problematic oil prices, restrictive sanctions and empty state reserve funds, in principle, lead to a logical continuation in the form of huge reforms. And naturally, one of these reforms should be an increase in taxes.
Of course, such prospects are never encouraging, because a Russian citizen already constantly lacks money for a banal existence. Expenses for paying for your own housing, utilities, food and clothing, as well as less obvious expenses in the form of travel fees and small but expensive necessities already greatly narrow the range of a person’s possibilities.
Especially today, in the unstable political situation with the past elections. It’s even scary to imagine what you can count on in 2021. Although for personal income tax the rate will most likely rise further and further. After all, even government organizations are happy to support such reforms.
The Ministry of Finance itself has already stated that, according to internal calculations, an increase in personal income tax by 2 percent will be quite significant for the state, since it will already bring half a trillion rubles in one year. These are very large numbers even for an entire country, since the entire budget as a whole consists of 3.5 trillion rubles. And if the reform is very important and profitable for the state, citizens can be patient.
But before we talk about the future, let’s go back and discuss what personal income tax actually is.
Taxation of interest on domestic marketable bonds is changing
By virtue of Law No. 58-FZ of April 3, 2021, from January 1, 2018, the procedure for taxing income in the form of interest on outstanding bonds of domestic firms and enterprises that have been issued for circulation since 2021 has been changed.
In fact, these interests are now subject to personal income tax as deposits in banks at a rate of 35% (new edition of clause 2 of article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Namely, the difference between the amount of interest payment (coupon) and the amount of interest, which is calculated:
- by bond par value;
- the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, increased by 5 percentage points and valid during the period of payment of coupon income.
Example
Interest on bonds owned by E.A. Shirokov, paid every year. The nominal value of the bonds is 2000 rubles. The Central Bank refinancing rate at the time of payment of income is 8.25%.
This means that 435 rubles will be subject to personal income tax:
2000 × 35% – 2000 × (8,25% + 5%)
Let us remind you that until 2021, the entire amount of income on outstanding bonds was subject to tax.
Attention!
The new procedure does not apply (letter of the Federal Tax Service dated July 24, 2017 No. BS-4-11/14422, information from the Federal Tax Service of Russia <On personal income tax taxation of interest on bonds>):
- for securities not traded on the organized market;
- income from any mutual funds;
- bonds denominated in foreign currency;
- bonds issued before 01/01/2017.
Then the tax is taken from the entire income of an individual.
Also see: Key Bet for 2021.
Personal income tax
PFDL is a direct type of tax, which is calculated as a percentage of the entire total income of an individual, excluding some documented expenses. Current legislation prescribes that absolutely all income that a taxpayer receives, be it sales or wages, is subject to personal income tax.
In general, the following representatives of the Russian Federation are taxpayers:
- individuals who are tax residents of Russia and stay on its territory for more than half of the calendar year;
- individuals who are not tax residents of Russia, but still receive taxable income on its territory.
In general, there are only five tax rates: 9%, 13%, 15%, 30%, 35%, which are set depending on the type of income that a particular taxpayer receives and the type of taxpayer himself. But as was said earlier, in many places there are now rumors about increasing tax rates for the next few years.
If you believe the numerous forecasts of various analysts and the media, then the personal income tax may well rise to as much as the fifteen percent mark. And the state itself says in this regard that the increase is completely justified and possible, just in some regions, where today there are significant shortcomings in the budget and financing of the subject.
Although for now the issue of personal income tax is, to put it mildly, up in the air, the same analysts and simply interested citizens are really building real budget plans and options for further development of the situation instead of simple assumptions. By 2019, tax reform may indeed quite logically occur in Russia, leading to an increase in the personal income tax rate.
Maybe these are all just assumptions without clear grounds and rumors on the spot out of nothing, but still citizens are clearly confident that the country will definitely undergo some changes in the near future. Recent events and statements by the State Duma fully confirm all these fears, so we can already talk about changes, at least using the example of personal income tax.
What does economic theory say?
Anyone who has been professionally involved in economics knows that, other things being equal, an increase or decrease in the tax burden reduces or increases the level of GDP, but not its medium-term pace.
If the tax burden increases, then the level of GDP decreases and the budget receives significantly less additional taxes than follows from direct arithmetic calculations. The reason for this effect lies in the fact that government spending is largely unproductive, and public investment is less efficient than private sector investment. If the tax maneuver is used to redistribute the burden between households and the corporate sector without increasing this burden, then there will be a restriction of consumption in favor of investment. But we must not forget that in Russia the level of savings is at an acceptable level, and the level of investment in GDP is lower due to unresolved acute structural problems and a poor investment climate. In addition, the level of consumption in the country is not that high, and effective mechanisms for supporting disadvantaged families have not yet been created.
Therefore, an attempt to transfer the tax burden in this way will lead to a reduction in consumption, but investment will still not increase due to the low solvency of households. The result will not be long in coming: economic stagnation will continue, and the need to increase budget spending on ineffective anti-poverty programs will also increase.
Personal income tax rates in 2021
Today, personal income tax rates seem quite shaky, as do the KBK for personal income tax, standard tax deductions for personal income tax or personal income tax refunds for past years, but you shouldn’t worry so much right away. No one can say for sure what changes await us, not even the state itself and its numerous representatives, represented by the State Duma or, for example, the Ministry of Finance.
For now, the country has established a moratorium on any increase in tax rates, as this will greatly change the tax burden of Russia as a whole. Personal income tax consists of five rates established for all types of income that the taxpayer receives. The Tax Code establishes all the basic principles of tax management. But still, in the near future we can still expect a sharp increase or decrease in the rate by a couple of percent.
Let’s look at all the rates separately in order to have at least some idea of personal income tax and the differences between various tax penalties in Russia.
Rate 9%
This is the smallest of all rates, its size is only 9 percent of the total income of an individual. It applies to cases such as:
- making a profit, such as any dividends;
- all interest payments on various bonds that were issued before 2021;
- the constituent income of a mortgage-backed trust that was received under certificates issued before 2007.
Rate 13%
This rate is slightly higher than the previous one and its size is only 13 percent for individuals who are tax residents of the Russian Federation. Taxable income includes:
- various dividends;
- official salary of a citizen;
- any monetary rewards under contracts;
- all profits received from the disposal or sale of one's personal property.
There are no tax deductions for income received as a result of a citizen’s share participation.
If the taxpayer is still not a citizen of the Russian Federation, but receives income on its territory, then the NFDL also applies to him. Here the taxable income is:
- official income received from various activities;
- all remunerations of crew members of ships flying the flag of the Russian Federation from labor relations;
- payments for the work of a qualified specialist who is not a citizen of Russia;
- all income of individuals who have moved and permanently reside abroad.
The entire 13% rate is paid by any citizens of other states, persons without citizenship at all and temporary citizens of any country who officially conduct some kind of activity in Russia and receive the corresponding official income.
Rate 15%
This tax rate is established for most individuals who receive wages in the form of dividends from domestic organizations. Only these persons must be foreign citizens.
Rates 30%
All other income that is not included in the list available to tax residents of the Russian Federation must be taxed at a rate of 30%.
Rate 35%
But the highest rate in personal income tax is as much as 35%, which is quite a lot, considering what kind of income is taxed. Eligible income is:
- prize money and various winnings;
- interest payments on various bank deposits;
- interest on borrowed funds that goes beyond the norm;
- payment to a credit consumer cooperative.
In general, it is very important to consider that any individual who receives official income taxed at a rate of 13 percent can greatly help himself. This assistance is called deductions, which is understood as an amount that reduces the amount of all income for the reporting period. And the Tax Code defines all deductions as “the return of a certain part of the personal income tax already paid.”
Personal income tax - what are the tax rates this year?
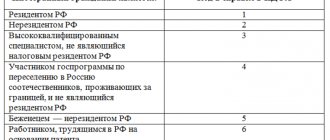
For the majority of our fellow citizens, the thirteen percent rate of this tax is the basic one. Many people simply do not know about any other values of this indicator. So, the range of these tax deductions varies quite widely - from nine to thirty-five percent. Let's try to at least superficially familiarize ourselves with each of the five existing personal income tax rates.
Payers of the nine percent income tax include:
- holders of mortgage-backed bonds, the issue of which dates back to the beginning of 2007. Tax is levied on the interest on these securities;
- founders of trust management with income from mortgage-backed participation certificates issued before January 2007.
The thirteen percent tax is addressed to the following category of taxpayers:
- citizens of the Russian Federation who receive income from their work activities in the country;
- persons classified as highly qualified specialists;
- participants of the state program for assistance to compatriots living outside of Russia, as well as their relatives who have expressed a desire to return to their homeland;
- all foreign citizens and stateless persons, as well as refugees who have been granted temporary asylum by the state, working and earning income within the country;
- crew members of sea vessels flying the Russian flag.
A fifteen percent tax is imposed on recipients of dividends from the activities of companies registered in the Russian Federation, provided that they are among their shareholders.
A 30 percent tax is imposed on income from securities, except for dividends specified in the previous paragraph and income with a different tax rate:
- foreign nominal and authorized holders of securities whose accounts are opened within the framework of depository programs of Russian banks;
- in case of failure to provide information about income to the tax office, in accordance with the requirements of Article 214, paragraph 6 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Changes
Well, now it’s time to talk about those very tax changes that may be awaiting us in the near future. Because even now there is some information or guarantors that confirm the possible fears of all Russian citizens. Let's look at the main upcoming changes to personal income tax.
- In 2021, a significant extension of the exemption from personal income tax is provided for all payments or monetary objections to citizens who are self-employed and do not conduct business activities. This will also affect employers, who are exempt from paying all insurance premiums received as a result of payments to self-employed citizens of the Russian Federation.
- They are also considering a new bill that will lead to the abolition of personal income tax next year for the sale of household waste paper. If the documents for this project are approved and signed on time, then from January 2021 we will see it in action.
- From the State Duma, the Communist Party faction sent the Chairman of the State Duma a certain bill, which is intended to change Chapter 23 of the second part of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. They put forward an initiative to set absolutely different rates. This could also be implemented by early next year.
- Already on April 23, 2021, a law came into force that regulates personal income tax payments for each month. However, this will only be carried out at the birth of children: the first and second.
The President of the Russian Federation Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin himself instructed those responsible to develop and implement a variety of numerous proposals related to reforms of the state tax system. Now in 2021, work is already underway on future changes in 2021.
If you believe the president’s words, the main goal of all future reforms will be to stimulate the economy and move towards business activity of the entire population of the country. Analysts say that all important changes will concern personal income tax rates. But it's not that simple.
Updating the declaration in form 3-NDFL
Also, the Russian Tax Service has prepared changes to the personal income tax return form in form 3-NDFL. It was approved by order of the Federal Tax Service dated December 24, 2014 No. ММВ-7-11/671. Apparently, the updated 3-NDFL form will be introduced in 2021, including for reporting for 2021.
So, we received a new edition:
- title page of the 3-NDFL declaration;
- Sheet D1 “Calculation of property tax deductions for expenses on new construction or acquisition of real estate”;
- sheet E1 “Calculation of standard and social tax deductions”;
- Sheet 3 “Calculation of taxable income from transactions with securities and transactions with derivative financial instruments (DFI)”;
- Sheet I “Calculation of taxable income from participation in investment partnerships.”
There are also amendments to other sheets of 3-NDFL.
In addition, the 3-NDFL declaration received a completely new sheet K entitled “Calculation of income from the sale of real estate.”
Also see “What documents to attach to the 3-NDFL declaration.”
How to calculate tax
If suddenly, behind all these complex changes, taxpayers will have questions like: “How will personal income tax taxes be calculated then?” or “What is this, recalculating everything now?”, then you shouldn’t rush to conclusions. Maybe even big changes will not affect the rates themselves, but will only change some aspects.
So for now you don’t have to worry about calculation formulas and spreadsheet accounting systems. If there are any changes in this area, then the Ministry of Finance will certainly inform about this in advance in order to prepare all organizations, entrepreneurs and employees themselves.
If there are those who are still wondering about the calculation of personal income tax without changes, then all the detailed information can be easily found on the Internet, without even having difficulty finding what you need. Why are there examples and diagrams? There are even online calculators that should accurately calculate all taxes. So there was no need to worry about the availability of information, and there is no need to worry in the future.
In general, in order to understand how much all the upcoming changes will affect ordinary citizens of the state, we must wait and see what the state will come to in these matters. So you shouldn’t judge too hotly; maybe many reforms will only bring sweet fruits.