According to statistics, at the beginning of 2021, there were just under 44 million people living in Russia who are eligible to receive pension payments. This is a very impressive figure relative to the entire population in the country. However, these statistics do not take into account recipients of military pensions.
In general, pensioners are usually considered to be elderly citizens who receive cash payments based on their length of service. In this case we are talking about recipients of an insurance (formerly labor) old-age pension.
Indeed, the overwhelming majority are among pensioners. However, there are other types of material and monetary support that certain categories of citizens can count on. In particular, now we will talk about the features of the state pension, aspects of the assignment of which are regulated by the relevant federal law.
Basic provisions of Federal Law 166 on state pension provision
State provision of a pension should be understood as a form of material support for special groups of citizens and members of their families, which is compensation for lost earnings due to reaching a certain age, loss of ability to work due to illness or injury, as well as upon achieving sufficient length of service.
Issues related to determining the circle of persons who can count on state security, as well as the basis and procedure for its appointment, are regulated by the Federal Law of December 15, 2001 “On State Pension Security in the Russian Federation” No. 166-FZ.
This normative act was adopted by both houses of Parliament and signed by the President at the end of 2001 . However, its main provisions came into force on January 1, 2002. Today the law is in force, and its norms are subject to application throughout the Russian Federation.
Structurally, the normative act under consideration consists of 28 articles, which, in turn, are combined into 6 chapters. In addition, annexes to it are an integral part of the document.
Let us examine in more detail the brief content of each chapter.
Chapter 1
Contains the main provisions, revealing the essence of this regulatory act. Separate articles introduce special terminology and concepts that are used in the law. In addition, the persons entitled to this type of security are specified and the types of state pensions are established.
Important! The list of categories of persons specified in Article 4 of the federal law in question is exhaustive.
Chapter 2
The norms of this chapter establish the grounds for assigning the type of financial support in question for each category of persons who have the appropriate right.
Chapter 3
Chapter 3 establishes the amount of pensions for various categories of citizens who, by virtue of the law, can apply for payments.
Chapter 4
The norms of this chapter introduce such concepts as “work experience”, “civil service experience” and “average monthly earnings”. In addition, the procedure for calculating length of service and earnings is established accordingly.
Chapter 5
The rules of this chapter regulate the procedure for establishing material support, payments, organizing delivery, indexation and recalculation (if grounds for this arise).
Chapter 6
This section contains rules establishing the procedure for enacting federal law and defining some special provisions.
Annex 1
Contains a table indicating the age when citizens employed in public administration can go on vacation.
Appendix 2
This appendix contains a table of the length of service of civil servants, in the presence of which this category of citizens can count on the assignment of monetary support.
Reference! Official publications and websites of information and legal systems contain a list of regulations amending this law.
Control of savings according to Federal Law-166
The law on state pensions in the Russian Federation provides for two types of pension contributions - insurance and savings contributions.
The second type can be transferred for management to special structures, private or public funds, whose activities are aimed at increasing the investor’s funds. A citizen has the right annually:
- change the insurance company handling the funded part of his pension;
- move from private funds to public funds regulated by the Pension Fund;
- request information about the state of accumulated funds and the profitability of the management company.
According to Federal Law-166, in order to carry out the above actions, you must personally contact the territorial office of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation with an application according to the sample.
Conditions for assigning a pension according to law 166
The payments discussed in this article are assigned to various categories of citizens. Accordingly, the grounds and conditions for the appointment will also be different, and the relevant provisions may only be applicable to a specific group of pension recipients.
Next, we will analyze in detail the grounds and conditions for assigning financial payments to various categories of pensioners, guided by Art. Art. 7-13 of the federal law.
Federal civil servants
Civil servants working in federal departments have the right to receive financial support if they have the appropriate length of service . It should be noted that the pension reform also affected this category of persons.
In this regard, the requirements for the length of service of civil servants are growing every year. Thus, until 2021, to receive money it was necessary to work for at least 15 years. In 2021, the number of years of service must be at least 17. The most stringent requirements for length of service will be established after 2026, when civil servants begin to go on vacation, subject to working for at least 20 years.
Cosmonauts and test pilots
Cosmonauts have the right to count on receiving government support if they have served at least 25 years for males and 20 years for females. At the same time, there are also requirements for the number of years spent in aviation units (10 and 7.5 years for men and women, respectively).
Similar requirements for length of service are imposed on test pilots, however, if they leave this type of activity due to deteriorating health, they can count on receiving pension payments even if they have fewer years of service (20 and 15 years for men and women, respectively).
Military personnel
The assignment of pension money to army and navy employees has certain specifics. The procedure for assigning state payments to the military, as well as other employees of law enforcement agencies, is established by the relevant federal law, which is expressly stated in paragraph 1 of Art. 8 of the federal law.
Veterans of the Second World War and survivors of the siege
It has been established that , as well as citizens with the status of “resident of besieged Leningrad” who have been diagnosed with a disability, have the right to special material support from the state
Persons affected by man-made (including radiation) accidents
For the most part, we are talking about the so-called “Chernobyl victims” - citizens whose lives and health were, in one way or another, affected by the Chernobyl accident.
Thus, persons who are directly involved in work at a nuclear power plant or suffered as a result of the liquidation of a disaster go on vacation at 55 and 50 years old, if they have worked for at least 5 years. Citizens who have become disabled become pensioners at 50 and 45 years of age if they have similar work experience.
Attention! Certain pension benefits are available to citizens living in resettlement zones and with the right to resettlement.
Social pension
can count on a social pension due to their respective status or upon reaching a certain age:
- disabled people (including disabled children and disabled minors);
- representatives of small northern peoples who have reached the ages of 55 and 50 years.
In addition, elderly citizens who, for one reason or another, do not meet the criteria for an insurance pension can count on social benefits. Social benefits are assigned 5 years later than the insurance pension.
Control of savings according to Federal Law-166
All Russians who have a funded part of their pension have the opportunity to transfer it to the management of certain structures.
Pension financial assets can be managed by:
- Pension Fund of the Russian Federation (abbreviated as PFR):
- a market management company with which, based on the results of the competition, the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation entered into a contract or Vnesheconombank;
- non-state fund - NPF: it performs the functions of compulsory pension insurance.
You can change your insurer and management company every year if you wish. To do this, you need to submit an application to the territorial office of the Pension Fund at your place of residence.
Types of savings according to the pension law
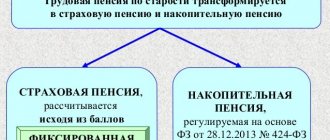
Future state payments are summed up from insurance and funded pensions. There are three types of insurance compensation - old age, loss of a breadwinner or disability. In Russia, residents upon reaching 60 years of age for men and 55 years of age for women can apply to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation and begin receiving compensation.
Insurance compensation is collected from pension points and has a complex formula depending on length of service. The Russian government sets the value of the pension point every year. A funded pension is the result of savings accumulated at the time of retirement.
Important! A citizen has the right to choose whether to receive a lifetime or immediate payment
- Decree of the President of the Russian Federation dated May 15, 2018 n 215
Pension amounts
The size of the state pension may vary for different categories of recipients.
- Civil servants. Federal officials receive a pension of 45% of their average monthly salary. It should be noted that if a civil servant has more length of service than is required for retirement, then for each “extra” year 3% of his average earnings is added to his pension.
- Military personnel. The army pension depends on material allowances in the last years of service, as well as some other conditions. Art. 15 of the normative act under consideration also establishes the amount of financial support for military personnel who have become disabled, as well as payments to family members of a deceased military man. It directly depends on many factors related to the form of military service, the nature and severity of the reasons that led to the impossibility of further service in the ranks of the Armed Forces or death.
- Veterans of the Second World War and survivors of the siege . Thus, for WWII veterans the amount is (as a percentage of the established social pension): Group I - 250%; Group II – 200%; Group III – 150%. For citizens, former residents of besieged Leningrad: Group I - 200%; Group II – 150%; Group III – 100%.
- Persons affected by radiation and man-made accidents. The amount of payments to these persons also depends on the amount of the social pension. In the vast majority of cases it is 250% of it. This applies not only to those related to the Chernobyl nuclear power plant, but also to those affected by other force majeure circumstances of this nature. Citizens living in the contaminated area are paid 200% of the social pension.
- Cosmonauts and test pilots. Cosmonauts, if they have sufficient length of service, receive a pension in the amount of 55% of their salary. Pilots can count on a pension of 1000% of social security.
- Social pension. The basic social pension in Russia at the beginning of 2021 is 5283.85 rubles. Some other categories of citizens can also count on the same amount of security.
The circle of persons entitled to receive two pensions simultaneously
The right to simultaneously receive two pensions is granted:
- for citizens who have become disabled due to military trauma:
- disability pension;
- old age insurance pension;
- participants of the Great Patriotic War:
- disability pension;
- old age insurance pension;
- parents of military personnel who served in conscription, died (died) during military service or died as a result of a military injury after dismissal from military service (except for cases where the death of military personnel occurred as a result of their unlawful actions):
- survivor's pension and old-age (disability) insurance pension;
- survivor's pension and social pension (except for social survivor's pension);
- survivor's pension and long-service pension (for disability), provided for by the Law of the Russian Federation of February 12, 1993 N 4468-I “On pension provision for persons who served in military service...”);
- to widows of military personnel who died during conscription as a result of military trauma and who did not remarry:
- survivor's pension and old-age (disability) insurance pension;
- survivor's pension and social pension (except for social survivor's pension);
- survivor's pension and long-service pension (for disability), provided for by the Law of the Russian Federation of February 12, 1993 N 4468-I “On pension provision for persons who served in military service...”);
- disabled family members of citizens who received or have suffered radiation sickness and other diseases associated with radiation exposure as a result of the disaster at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant or work to eliminate the consequences of this disaster; those who became disabled as a result of the disaster at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant; who took part in the liquidation of the consequences of the disaster at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant in the exclusion zone:
- survivor's pension and old-age (disability) insurance pension;
- survivor's pension and social pension (except for social survivor's pension);
- citizens awarded the badge “Resident of besieged Leningrad”:
disability pension and old-age insurance pension; - federal civil servants:
simultaneous receipt of a long-service pension and a share of the old-age insurance pension established in addition to the specified long-service pension in accordance with the Federal Law “On Insurance Pensions”. - military personnel (with the exception of citizens who served in conscription)
simultaneous receipt of a long service pension or a disability pension, provided for by the Law of the Russian Federation of February 12, 1993 N 4468-I “On pension provision for persons who served in military service...”, and an old-age insurance pension (with the exception of a fixed payment to the insurance pension), established under the conditions and in the manner provided for by the Federal Law “On Insurance Pensions”.as soldiers, sailors, sergeants and foremen) if there are conditions for assigning them an old-age insurance pension provided for by the Federal Law “On Insurance Pensions”:
- citizens from among the astronauts
simultaneous receipt of a long service pension or a disability pension provided for by this Federal Law, and an old-age insurance pension (with the exception of a fixed payment to the insurance pension), established under the conditions and in the manner prescribed by the Federal Law “On Insurance Pensions”.if there are conditions for assigning them an old-age insurance pension, provided for by the Federal Law “On Insurance Pensions”:
- citizens from among the flight test personnel have the right to simultaneously receive a long-service pension provided for by this Federal Law and a share of the old-age insurance pension established in addition to the specified long-service pension in accordance with the Federal Law “On Insurance Pensions.”
Pensions provided for by this Federal Law are established and paid regardless of the receipt of a funded pension in accordance with the Federal Law of December 28, 2013 N 424-FZ “On Funded Pension”.
Types of pension payments for state provision
Article 5 of the regulatory act under consideration identifies the following types of payments:
- For years of service.
- Due to disability.
- For the loss of a breadwinner.
- Due to old age.
- Social payment.
It has been established that state payments due to lack of ability to work, old age and loss of a breadwinner are received by persons who cannot count on receiving insurance-type pension payments. As a rule, this is due to non-compliance with the criteria for the IPC and the insurance experience of citizens.