The world's largest economies for 2021. Top 20 according to the IMF
There are two approaches to determining the world's largest economies.
First, assess the size of a country's economy by nominal GDP (gross domestic product) - the total value (in US dollars) of goods and services produced during the year in all sectors of the country's economy. However, prices in developed countries are noticeably higher than in developing countries (as an example, the Big Mac index, according to which a Big Mac in Switzerland costs 10 times more than in Venezuela), therefore the nominal GDP of developed countries is overestimated, and the nominal GDP developing countries is underestimated. To solve this problem, the concept of “purchasing power parity” (PPP) was introduced into economics, according to which GDP is estimated adjusted to the level of current prices in the country’s economy. Based on the presence of two approaches to assessing the size of the economy, one can come across contradictory statements about the Russian economy, since in terms of nominal GDP Russia does not even fall into the top ten largest economies, however, in terms of GDP at purchasing power parity, Russia is among the top five largest economies in the world and is in first place in Europe. Currently, economists prefer the second approach as more reliable. For example, since 2020, the IMF has refused to calculate the nominal GDP of countries and began to publish only economic data based on PPP. In this review, we will look at the top 20 largest economies in the world based on both approaches: by GDP at PPP (IMF data for 2021) and nominal GDP (IMF data for 2021)
Economy of Italy
Italy is an agricultural country that has managed to establish both the production of agricultural products and sell them around the world, and heavy engineering. A significant share of income comes from tourism.
Rice. 3 Tourists in Rome
Developed countries of Foreign Europe have a share of more than 30% in global industry. They have one of the highest per capita incomes. These states are engaged in science, studying new technologies and successfully implementing them, thanks to which they manage to remain leaders in scientific and technological progress.
The strongest economies in the world
Economic cycles and changes affect individual countries differently, but leaders tend to maintain their positions in all conditions. The world's strongest economies have not changed dramatically since 1980. Only 3 new states appeared in the top twenty.
Moreover, key players hold the majority of the world's wealth. The top ten economies account for 68% of the world's nominal GDP, while the top twenty account for 81%. The remaining 172 countries produce less than 1/5 of global economic output.
USA
- Nominal GDP: $21.44 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $21.44 trillion
The United States has maintained its status as the world's leading economy since 1871. In 2019, in nominal terms, its volume amounted to $21.44 trillion. In 2020, $22.32 trillion is predicted.
This country is often called an economic superpower because it makes up almost ¼ of the world economy and is distinguished by the development of infrastructure, technology, and an abundance of natural resources. And this despite the fact that 80% of the country's gross domestic product comes from the service sector.
When assessed on the basis of purchasing power parity, the United States loses first place to the People's Republic of China and lags behind by $6 billion. According to Navy forecasts, the gap will widen, and by 2024 the United States will have $25.79 trillion, and the PRC will have $39.81 trillion.
Division of European countries based on development
If we consider the entire European continent, then only 2 categories of countries are represented here: developed and with economies in transition.
The first group includes all countries of Western Europe, the second group includes the former countries of the socialist camp. The transitional nature is due to the fact that their economy has not yet fully switched to market methods of running the national economy. There are no formally developing countries on this continent, but there are national economies and social conditions at different levels. For example, subcategories such as developmentally delayed are identified.
These include Spain, Portugal and Greece. There are the so-called G7 countries, which occupy a leading position in the world economy. These are France, Germany, Italy, Great Britain.
China
- Nominal GDP: $14.14 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $27.31 trillion
The strongest economies in the world cannot do without the Celestial Empire. Over the past few decades, China has achieved exponential growth by overcoming the barriers of centralized closed trade. It is now a manufacturing and export center, sometimes called the "factory of the world."
In 1980, China was in the TOP 20 in seventh place with $305.35 billion in GDP. The US then had $2.86 trillion. Thanks to reforms begun in 1978, China actually began to increase its GDP by 10% every year. Recently, these rates have slowed, although they remain very high.
The World Bank, speaking about the surge in China's economic growth in 2017, refers to the cyclical recovery in global trade. The organization predicted growth of 6.6% in 2021, and it was right. In 2021, growth was 6.1%. Gradually, by 2023, according to experts, it will decrease to 5.6%.
Due to its large population, China is not among the leaders in terms of GDP per capita - $19,500 (74th place in the world).
7. France
France consistently leads the lists of the richest countries in Europe and is a space and nuclear power. GDP per capita level is $42,400. Currently, the country is undergoing a process of transition from a state monopoly to market mechanisms while maintaining the existing level of well-being. The innovation sector is characterized by the predominance of foreign capital - its share is up to 40% in certain areas. The largest part of the GDP structure is accounted for by the service sector - 77.7%, small and medium-sized businesses are developed. The country has developed industrial production: mining, engineering, space, automotive, food, chemical. In terms of agricultural production, France ranks first in the European rankings: cheese, beef, wheat, and wine are produced in large volumes and are partially exported.
Japan
- Nominal GDP: $5.15 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $5.75 trillion
The 2008 financial crisis rocked the Land of the Rising Sun as it was accompanied by weak domestic demand and huge public debt. In addition, after the peak came out, a strong earthquake occurred, which hit the economy and social sphere. But by 2021, Japan's economy has surpassed the nominal GDP mark of $5 trillion. Forecast for 2021 – $5.59 trillion.
The Japanese economy will receive an additional stimulus for the 2020 Olympics, which always attracts investment to the host country. The strengthening is also facilitated by the Bank of Japan's tight monetary policy.
In 2021, GDP per capita was $45,550, the thirty-first figure in the world.
5. Norway
The GDP per capita is $62,510 per year. Norway is considered one of the best countries in Europe in terms of living standards, human development, and social security. This is made possible by the supervision of private companies: government control is combined with market activity. The public sectors of the economy are the oil, hydroelectric, industrial, banking, and telecommunications sectors. The principle that guides the state: hydrocarbons are the property of the nation. The country has developed metallurgical, pulp and paper and chemical industries, mechanical engineering, and fishing. Agriculture is focused on covering its own needs, and is based on meat and dairy production. Some products have to be imported, but in recent years the trend for export has been growing: Norway supplies Europe with strawberries and other berries that are not typical for the harsh northern country.
Germany
- Nominal GDP: $3.86 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $4.44 trillion
Germany has not only the largest but also the strongest economy in Europe. It is fourth in the world when assessed by nominal GDP. GDP at purchasing power parity is $4.44 trillion, and per capita is $53,570 (20th place). In 1980, the German economic volume was $850 billion, which was enough for third place in the ranking.
Germany was heavily dependent on the export of capital goods, and this increased the impact of the 2008 crisis. The economy grew 2.2% and 2.5% in 2021 and 2021. In 2021 and 2021 – by 1.5% and 0.5%. Forecast for 2020 – 1.2%.
Germany's continued economic strength is supported by the launch of Industry 4.0. This is a strategic initiative to create a leading market and provider of advanced manufacturing solutions to the world.
8. Netherlands
The Netherlands is a wealthy European state whose economy is characterized by its stability: the GDP per capita is $45,294, and production volumes are increasing every year. The percentage of unemployment and inflation in the country is low, without a tendency to aggressive growth. The most important industries are: mechanical engineering (including aircraft and shipbuilding), ferrous metallurgy, petrochemicals, textiles, pulp and paper, food, electronics and electrical engineering. Agriculture is developed, despite the relatively small number of areas suitable for this. Its peculiarity is the widespread use of greenhouses, careful cultivation of the land and a large amount of applied mineral fertilizers. Recently, the cargo transportation system has been actively developing in the Netherlands, including by land transport, but the main part is accounted for by ocean shipping.
India
- Nominal GDP: $2.94 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $11.33 trillion
India is the country with the fastest growing economy in the world, although it has been slowing down in recent years. In 2021, she took fifth place in the ranking from Great Britain. However, the GDP per capita of this country is far from its leading position - $8,380.
In 1980, the Indian economy was only $189 billion (13th place). In 2021 the economy grew by 6.8%, in 2021 by 6.1%. For 2021, the Navy forecasts growth of 7%.
4. Belgium
The top 10 richest countries in Europe include Belgium, which, thanks to its history and geostrategic position, is not only a highly developed industrial country: agriculture is also developing at a highly intensive pace. Some of the products are imported (cereals, exotic fruits), and some are exported: the production of meat, dairy (including eggs) and vegetable products exceeds the needs of the Belgians. The share of GDP per capita is $41,096, which is combined with a high percentage of unemployment - 10-7.2%: according to this indicator, Belgium is a leader among European countries. The basis of the economy is tourism and the service sector; industry (ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy, chemical production, mechanical engineering) accounts for 24% of GDP. The financial microclimate is attractive for foreign investment capital.
Great Britain
- Nominal GDP: $2.74 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $3.13 trillion
The United Kingdom ranks sixth in terms of nominal GDP, and ninth in terms of GDP based on PPP. The per capita income is $46,830, which puts the country 30th in the world. In 2021, nominal GDP reached 2.74 trillion; by 2023, $3.02 trillion is expected.
From 1992 to 2008, the British economy experienced upward trends in every quarter. However, since April 2008, a decline in production volumes has been recorded for five quarters. The economy shrank 6% during that time and took five years to return to pre-recession levels.
Three quarters of the UK economy's GDP comes from the services sector. The second most important segment is agriculture. Despite employing only 2% of workers, 60% of the UK's food needs are produced domestically.
3. Luxembourg
Luxembourg is one of the smallest countries in Europe, but one of the richest. The level of GDP per capita in Luxembourg is very high: $102,831 per year. Despite the fact that all energy sources are imported, industry, tourism and the banking system are developed here - these are the 3 pillars of the economy in the duchy. The country is home to Arbed (steel concern), SES-Astra (satellite telecommunications), RTL (television corporation). Luxembourg's liberal laws have allowed it to become the largest European investment center, and it also attracts foreign deposits from individuals. The share of agriculture relative to the total economy is low and tends to decrease. Viticulture, floriculture and horticulture are traditional for the Grand Duchy.
France
- Nominal GDP: $2.71 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $3.06 trillion
France is the most visited country in the world and has the third largest economy in Europe. It provides a high standard of living with a GDP per capita of $47,220.
Economic growth has slowed in recent years and, under pressure from rising unemployment, the government has had to develop a plan to reboot. In 2014-2016, the World Bank recorded an unemployment rate of 10%. By the end of 2021, this figure dropped to 8.5%.
In addition to tourism, which forms an important part of the economic system, France is one of the leading agricultural producers. It accounts for about a third of EU agricultural land.
The country ranks sixth in the world in terms of agricultural production and is second only to the United States in its exports. The manufacturing industry is dominated by the chemical industry, automobile manufacturing and weapons. All this helps France to be among the strongest economies in the world.
1. Iceland
Iceland opens the top ten richest European countries. The level of GDP per capita is 59,976.94 USD. The country has a low unemployment rate - even during the global financial crisis, this figure was 7.6%. The basis of the Icelandic economy is fishing and fish processing, and thanks to a competent, environmentally friendly policy, Icelandic fishermen are in the leading positions in terms of the amount of catch (up to 200,000 tons per year). The fleet is serviced by local ship repair yards and shipyards.
Iceland's second source of stability is hydropower and geothermal energy. The remaining areas are knowledge-intensive: the inhabitants of the island strive to make maximum use of natural renewable resources, thereby taking care of ecology and the environment. Local vegetables, dairy products and meat are supplied to the country's domestic market; only grains and some other crops are imported.
Italy
- Nominal GDP: $1.99 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $2.44 trillion
Despite its status as a significant member of the European Union, Italy is experiencing problems: unemployment is still about 10% (among young people - 28.6%), political and economic chaos is obvious in the republic. In addition, there is a public debt in the region of 144% of GDP.
But there is a resource for recovery, given stable exports and business investments. Growth of 1.1% and 1.7% was recorded in 2021 and 2021, and 0.9% in 2021. In 2021, GDP remained unchanged. For 2021, the IMF predicts +0.5%.
Brazil
- Nominal GDP: $1.85 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $3.46 trillion
Brazil is the largest country in South America by area and population. Domestic political uncertainty, corruption problems and the end of the so-called commodity supercycle have weakened the country's investment and business environment, but the situation appears to be improving.
In 2006-2010, Brazil gained an average of 4.5%, in 2011-2013 – 2.8%. In 2014, the growth was 0.5%. After a pullback of 3.3% in 2021, a growing trend has emerged again: +1.1% in 2021 and 2018, +0.9% in 2021.
3Norway
GDP $73.6 thousand
As promised, we are returning to Scandinavia, or more precisely to Norway. About 5 million people live in the country, and all of them are quite wealthy people, because the GDP per capita exceeds $70,000. Norway is famous not only for its high standard of living, but also for its safety. In 2011, a notorious man named Breivik did much to tarnish the idea of absolute calm in Norway, but today the country returns to its laurels as one of the safest in the world. As for economic affairs, the main source of replenishment of the Norwegian treasury is the oil and gas industry, which includes the extraction and processing of raw materials.
Canada
- Nominal GDP: $1.73 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $1.9 trillion
Canada displaced Russia from tenth place in the ranking in 2015 and still maintains its position. In 2021, nominal GDP reached $1.73 trillion, and by 2023 it is expected to grow to $2.12 trillion.
Despite the great importance of the service segment, 68% of exports are industrial products. Canada places a strong emphasis on industry as a key driver of future economic growth.
Russia
- Nominal GDP: $1.64 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $4.35 trillion
Russia is also one of the strongest economies in the world. Our country is the largest state, but only the eleventh in terms of nominal GDP. When considering GDP on a PPP basis, it is sixth.
The 1990s became a difficult period for the country's economy, which inherited devastated industry and agriculture.
In the 2000s, an increase of 7% was recorded, but this was due to the commodity boom. Energy dependence had a bad impact on Russia during the crisis times of 2008-2009 and 2014.
2016 ended with economic growth of 0.2%. In 2021, the country achieved growth of 1.6%, in 2021 – by 2.3%, in 2021 – by 1.1%. The Navy assumes that in 2021 Russia's nominal GDP will grow by 1.9%.
UK economy
The leading sector of the country's economy is the service sector, namely the banking system, serving the whole world. Per capita income is 41.5 thousand dollars. Britain also specializes in the production of electrical equipment, telecommunications, metallurgy, and food.
TOP 4 articles that are read along with this
- 1. German economy
- 2. UK Economy
- 3. Countries of Western Europe (list)
- 4. General characteristics of the countries of Foreign Europe
Rice. 2 Unemployment rates in European countries
South Korea
- Nominal GDP: $1.63 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $2.32 trillion
South Korea is known for such conglomerates as Hyundai and Samsung, but it is not only through their efforts that the republic has penetrated into the strongest economies in the world and has moved closer to the TOP 10. Over the past decades, the country has made incredible progress, becoming one of the global leaders in the field of high technology.
In the 1960s, South Korea was one of the poorest countries in terms of GDP per capita, and now ranks 32nd in the world for this indicator ($44,740). Industrialization and international trade already in 2004 brought it into the “trillionaire club.” In 2019, the South Korean economy grew by 2%.
Now it is one of the world's leading exporters. The country has also created excellent conditions for investing from abroad and doing business.
Rating of countries in the world by population
Population is an absolute value expressed in numbers that characterizes the total population of countries in the world in a certain period of time. One of the main demographic indicators.World population figures are calculated by the Population Division of the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UNDESA) based on statistics and estimates from national institutions and international organizations compiled by the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA). UN DESA's Population Division assesses historical population trends from 1950 to the present and also produces population projections up to 2100. These estimates are based on all available sources of data on the population of countries around the world and the main demographic components directly related to this indicator (fertility, mortality, international migration). National data sources include information from population and housing censuses in countries and regions over the past decade, information on birth and death registrations, demographic and health surveys, migration registers and other administrative sources of statistics. In addition to national data sources, international estimates from the following sources are taken into account: estimates of international migration flows and numbers of persons of foreign origin from the UN DESA Global Migration Database, statistics on refugees and displaced persons from the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR), Estimated time series of infant and child mortality from the United Nations Inter-Agency Child Mortality Estimation Agency (UNICA), various series of international estimates produced by international and regional organizations and academic research institutions. Population data from all sources are assessed for completeness, accuracy and consistency and adjusted as necessary.
The total population of the planet is constantly increasing, although its dynamics vary significantly in different countries (see Rating of countries in the world by population growth rate). According to UNFPA estimates, the total global population has exceeded the following numbers:
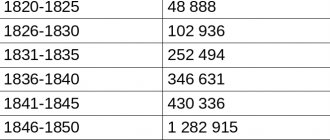
- 1 billion - in 1820.
- 2 billion - in 1927.
- 3 billion - in 1960.
- 4 billion - in 1974.
- 5 billion - in July 1987.
- 6 billion - in October 1999.
- 7 billion - in October 2011.
If the current dynamics of growth and decline in the planet's population do not undergo significant changes, then the milestone of 8 billion people will be crossed around 2024.
Population data for countries around the world is published annually in a special United Nations report entitled “Assessing World Population Trends.” Population figures are updated annually, but reports with UN data tend to be delayed by one to two years, as they require international comparisons after data are published by national statistical offices.
Spain
- Nominal GDP: $1.4 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $1.94 trillion
The Spanish economy consistently ranks 5th in terms of volume in Europe and is returning faster than Italy to the pre-crisis level of 2008. In the industry structure, 2/3 is occupied by services, 12% by industry, 2.3% by agriculture. One of the driving forces of the economy is tourism. Attendance in Spain has increased every year from 2009 to 2021.
Active growth is hampered by weakness in the information technology, electronics, and utilities sectors.
In 2021, real GDP growth was 3%, in 2021 – 2.6%, in 2019 – 2.2%. The IMF forecast for 2021 is an increase of 1.8%.
General characteristics of the typology of European countries
According to the current typology of countries, European countries can be divided into several groups according to the level of economic development.
The group of highly developed countries (G7 countries) includes four European countries - Germany, France, Great Britain and Italy. These are relatively large states in terms of area and population. They are characterized by a fairly high natural resource potential, a very high level of industrialization ($2-5$ times higher than the world average). All sectors of the economy are developed in these countries. Their share in global industrial production exceeds $40\%$, and in agriculture – $30\%$. Per capita income in these countries ranges from $20 to $30 thousand US dollars. These countries play an important role in international politics and economics. They are characterized by a high level of labor productivity and the level of development of science and technology.
Finished works on a similar topic
Course work Developed countries of Foreign Europe 470 ₽ Essay Developed countries of Foreign Europe 280 ₽ Test work Developed countries of Foreign Europe 190 ₽
Get completed work or advice from a specialist on your educational project Find out the cost
The small industrialized countries of Europe include Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Norway, the Netherlands, Sweden, Switzerland and Finland. Sometimes this group is also called “small privileged nations.” They, like highly developed countries, have a high level of industrialization ($2-3$ times higher than the world average). Natural resource potential is fully used in the economy. The structure of the economy of these countries may lack some industries and production. But the most important branches of scientific and technological progress - mechanical engineering, energy and the chemical industry - make up a significant share of global production.
Spain, Greece, Portugal, Iceland and Turkey form a group of countries that belatedly embarked on the capitalist path of development. Their economy retains some remnants of previous economic formations (for example, large landholdings and a multi-structured economy).
Note 1
A special group consists of the former socialist countries of Europe. They are called post-socialist countries in Europe with economies in transition, in which economic restructuring is taking place on a market basis. This group includes:
- Poland,
- Ukraine,
- Czech Republic,
- Slovakia,
- Hungary,
- Belarus,
- Romania,
- Moldova,
- countries of the former Yugoslavia.
Are you an expert in this subject area? We invite you to become the author of the Directory Working Conditions
They maintained an average level of economic development. Their social and economic life was determined for a long time by the command-administrative system. This hampered the development of productive forces. Today in these countries there is a transition from a totalitarian economic system to a market economy.
The level of industrialization of moderately developed countries has almost reached the world average. Most of these countries have significant natural, labor and economic resources. Over time, they can move into the category of highly developed countries.
Australia
- Nominal GDP: $1.38 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $1.36 trillion
Australia has the largest economy in the Pacific and the ninth largest securities exchange by market capitalization in the world. It has been steadily increasing GDP since 2009.
In 2013, the country was 12th in the world in terms of GDP, by 2021 it was overtaken by South Korea and Spain. But also in 2021, Australia was the country with the highest median wealth per adult.
In 2021, GDP growth was 2.4%, in 2021 – 2.7%, in 2021 – 1.7%. For 2021, the forecast is 2.3%.
At the beginning of 2021, catastrophic wildfires hit the country. It is still impossible to fully assess the damage, but this will definitely become one of the obstacles to GDP growth.
Mexico
- Nominal GDP: $1.27 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $2.63 trillion
In 2001, Mexico was the eighth country in the world by nominal GDP. By 2004, it fell out of the top ten, and by 2009, it settled in 15th place.
The oil industry plays an important role in the economy of this country. Therefore, in 2015-2016, under the influence of unfavorable dynamics of oil prices, Mexico's nominal GDP decreased by 18.8%. This was followed by growth, and the country almost “won back” the lost time.
According to the IMF, in 2017-2018 Mexico's GDP grew by 2-2.1%, in 2021 - by 0.4%. For 2021, the forecast is 1.3%.
Source