Spanish educational system
The structure of educational institutions of the state is under the strict control of the Ministry of Education, which approves standards for professional training of teaching staff, organization of the educational process, controls funding issues, etc.
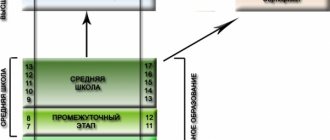
The stages of training are similar to the pan-European ones; they can be divided into several groups:
- Preschool (up to 6 years);
- Primary (6-12 years old);
- General secondary (12-16 years);
- Bachilerato or preparation for entering a university (16-18 years old);
- Secondary vocational (from 17 years old);
- Higher (from 18 years old).
If parents can study independently with children under 6 years old at home, then basic secondary education, in accordance with current legislation, is mandatory. Bachilerato, which is reminiscent of the senior classes of a Russian school, is also studied on a voluntary basis - mainly by those who plan to receive higher education. Note that the initial and intermediate levels can be completed free of charge, subject to visiting a government institution, for both Spaniards and children from foreign families.
What free education is provided in Spain?
According to the Spanish Education Law, basic primary education in the country is free and compulsory for all citizens.
Basic education refers to primary school and secondary education. Thus, free education in Spain is possible only until the student is 16 years of age . Children of foreigners living in Spain are required to receive secondary education also free of charge.
It is possible to get a higher education at universities in Spain for free, but it is very rare. The availability of such an opportunity must be checked with the university on a case-by-case basis. Only Spaniards get this chance.
All kinds of grants and scholarships are also predominantly received by Spaniards. Therefore, free higher education is impossible for Russians in Spain.
Structure of higher education in Spain for Spaniards and foreigners
The university has three stages of preparation:
- Bachelor's degree (grado). The duration depends on the chosen direction; most professions are mastered in 4 years. Doctors, architects, lawyers, veterinarians and some other specialists study the longest.
- Master's degree. A highly specialized course lasting 1-2 years, upon completion you need to defend a diploma.
- Doctorate (doctorado). An analogue of Russian graduate school with a doctorate degree and the right to work in the department, teach, write a dissertation and engage in research activities. Takes 3-6 years.
Thus, Russians who want to enroll in a university in Spain first need to decide what the level of knowledge they possess is called and choose the level of study at the university. It will not be possible to “jump” from one to another, since when submitting documents you will have to document the acquired level of knowledge. That is, you can apply for a master’s degree only if you have a diploma of completion of a bachelor’s degree, etc. Graduates of Russian institutes can also continue their studies in one of the institutions of the Kingdom, but to do this they will need to have their certificate translated and, in some cases, homologated, as well as pass entrance exams and a language test.
Structuring higher education
The higher education system in the country consists of 3 levels, at the end of each of which students are awarded a corresponding degree.
The levels and features of Spanish education are presented in the table:
| Learning cycles | Time spent (in academic years) | Technical specialties | Architects | Other professions |
| First: bachelor's degree. Prospects – work activity with a weak level of career growth. | 4 | Ingeniero tecnico | Arguitecto tecnico | Diplomado |
| Second: master's degree. Prospects – deep specialized knowledge. | 1-2 | Ingeniero superior | Arcuitechto | Licenciado |
| Third: graduate school. Opportunity to continue scientific activities. | 2 | 2 years of study include the preparation of a dissertation, after a public defense of which the degree of Doctor of Science is awarded. | ||
What is needed for admission to a bachelor's degree?
The reasons for inclusion in student lists are generally the same for Spaniards themselves and for foreigners. The only difference for Russian applicants will be the need to demonstrate language proficiency at the proper level. Ideally, have a DELE or SIELE certificate, which are recognized in all training centers and are often exempt from examination tests. Otherwise, you can already take language courses on the spot, especially since they are often included in the preparatory program for foreigners organized by the higher school. In addition, to enroll in a Spanish university, a foreign student will need to homologate, that is, translate and confirm, a school certificate. Finally, you need to collect a package of documents that must also be translated and, in some cases, apostilled (see below for a detailed list).
Thus, the algorithm of actions for those wishing to study at a university in the Kingdom looks like this:
- Select a direction (one or more).
- Find out the exact requirements by studying the institution’s website and talking with the coordinator.
- Collect and prepare a portfolio.
- Pass the required exams.
- Apply online on a single platform.
- Wait for the results and, after a positive decision, officially confirm your intention to study.
- Provide original documents.
- Obtain a visa to enter the country and register for student residence.
Benefits of studying in Spain
Education in a Spanish state is an excellent opportunity for foreign applicants to gain experience living in a European state. The average cost of studying at prestigious local universities is significantly lower compared to other European universities. Additional benefits of studying in Spain are:
- the opportunity to learn or improve Spanish, the second most widely spoken language in the world;
- a large selection of educational programs in English;
- the right to immigrate with family - spouse and minor children;
- good chances of employment in prestigious companies after graduation (diplomas from Spanish universities are highly recognized throughout the world).
It is worth mentioning the disadvantages of being a student in Spain. Many students are not satisfied with the opportunity to work no more than 20 hours a week, and study visa holders receive the right to enter into full-time employment contracts only after 3 years of stay in the country. There is also no complete confidence in the issuance of the visa itself: the reason for refusal to cross the border is the presence of a criminal record in the homeland or being on the stop list for entry into the country.
Still have questions? our lawyers will advise you free of charge by phone
What study programs are offered at universities in Spain for Russians, including free of charge?
When going to the Kingdom, you are practically unlimited in choosing your specialty. Dozens of public and private higher, professional and business schools offer both classical and cutting-edge areas. The most popular disciplines are:
- Medicine
- Biometric engineering
- Information Technology
- Economics and Management
- Business Administration
- Entrepreneurship and Management
- Design
- Advertising and PR
- Architecture
- Right
- Pharmaceuticals
- Journalism
- Geology
- Mathematics
- Sociology
- Fashion Marketing and Communication
- Physics
- Biochemistry
- Marine biology
- Engineering
- Tourism and hotel management
- Graphic design
Recently, so-called “double” specialties have come into fashion, being at the intersection of disciplines, which significantly expand the opportunities for graduates to find high-paying and promising jobs. Among the most popular are mathematics and physics, business administration and law, art and design, biology and biotechnology, and others. It is also worth noting that master’s and doctorate degrees provide more highly specialized knowledge.
How to collect documents for a Russian to enter a university in Spain after school for free
Let’s immediately make a reservation that studying at universities in the Kingdom is paid for both foreigners and citizens of their own country, the only difference is in the prices. However, for the most talented applicants, there is a system of scholarships and grants paid for by international or Russian educational foundations, which allows even students without funds to study. Grants are published annually on university websites with all requirements and application deadlines. Typically the list of papers includes:
- school certificate, translated and homologated, that is, officially confirmed;
- certificate of language proficiency;
- passport;
- motivation letter – written in free form, not always required;
- application – submitted in electronic format, filled out online.
It is worth remembering that applications are usually accepted in 2-3 streams, while foreign candidates may be allocated a separate period: it is recommended to inquire about the deadlines from the project curator. In this case, it is allowed to submit a request simultaneously to several educational institutions.
Private Universities in Spain
In private universities, it is possible to study and take entrance exams entirely in English. To enroll in a private university in Spain, you need to pass an online interview with the university commission, write a motivation letter and provide a certificate of language proficiency. In such universities, teachers focus on developing the student’s personal qualities; the universities cooperate with international companies where one can get internships and help to establish social connections.
What is Selectividad?
To enter a university in Spain, both Spaniards and Russians need to pass an entrance exam, held twice a year. There are currently three types of testing in the country:
- PAU (Pruebas de Acceso a la Universidad) - a single examination test for all Spaniards, as well as foreigners, who want to study in Barcelona and Valencia;
- PCE (Pruebas de Competencias Específicas) - an analogue of PAU for foreign applicants, conducted by the National University of Distance Education (UNED), it can be taken in absentia;
- EbAu (Evaluación de Bachillerato para el Acceso a la Universidad) is another type of PAU most often requested by Madrid institutions.
PAU, formerly called Selectividad, like its other variations, is always conducted in Spanish and consists of two parts: compulsory and optional. In the first part, applicants undergo a language test and a test of basic knowledge in specialized disciplines, depending on the chosen specialty: for example, future engineers take mathematics, physics and drawing, and to study at the Faculty of Medicine, “savvy” in chemistry and biology is required. The overall score for admission is based on the results of the tests passed and the average score of the school certificate. If a student wants to improve his chances of being accepted, he can take several other electives.
It is worth noting that it is very difficult to successfully pass the test without preparation, so many Spaniards take special courses for admission. Typically, such programs last about a year, although recently intensive courses lasting from one to three months, as well as individual classes, have become increasingly popular.
Requirements for admission to universities in Spain
Entrance points system
Each department of any Spanish university, private or public, has its own passing score. In the Spanish educational system this is called Notes de corte. All this is calculated according to a rather complex scheme with coefficients for each stage.
We will tell you more about the formula and how to calculate your score in a separate article dedicated to Selectividad and entrance exams. In short, Notes de corte consists of three components: the grades of the certificate are taken into account (in the Spanish education system this is bachillerato), the results of entrance tests to the university and the average score of the Spanish analogue of the Unified State Exam - Selectividad. And although now this exam has other names - EvAu, PAU and PCE, in Spain they still continue to call it by their old name out of habit.
The highest passing score for doctors is 14, the lowest possible is 5 in the faculties of tourism and humanities. Despite the fact that the highest grade in a Spanish school is 10, some universities count additional points for excellent knowledge in subjects important to the department.
So it turns out that the passing grade is higher than the highest grade. If the passing score is low, this means that there is little competition for this department, and, quite possibly, there are no entrance exams. You can get advice directly from the university where you would like to study.
If you still decide to enroll in one of the public universities in Spain, despite the harsh selection of future students, you need to fulfill a number of conditions. They depend on who you are: a graduate with an 11th grade certificate, a student at a domestic university, or a graduate with a higher education diploma. This determines which route of admission to a Spanish university you choose.
The first and general stage for everyone
Recognition of your certificate or diploma by Spain. For admission, you must confirm (Homologación or Equivalencia) your educational document. Following the logic, this must be done before entering a university in Spain. But given that the admissions campaign begins almost immediately after receiving the certificate, the management of Spanish universities accepts for consideration a translated and certified copy of the certificate and your request for homologation with the appropriate mark from the Ministry of Education and Vocational Training.
The most reliable and detailed information can be obtained on the official website www.educacionyfp.gob.es.
What does it mean to homologate a diploma? This means that your diploma/certificate is recognized as the same as that of the corresponding institution in Spain. Equivalence (in case of admission) is recognition of your previous education by the educational institution itself. After reviewing it, you will be informed which subjects you need to study additionally. This is the first stage and the first term of Notes de corte.
Your next steps depend on who you are: a former school student, a student at a Russian, Ukrainian, Kazakh university, or a graduate of a higher educational institution who wants to get a master's degree in Spain.
Second stage: If you are a graduate of a secondary school.
So, you dream of studying at a public university in Spain and you only have school education behind you. To begin with, you need to learn Spanish to level B2. This is a fairly advanced level that will allow you to learn in this language.
You also need to remember that to enroll you must pass the Spanish equivalent of the Unified State Exam - Selectividad. Because to date, an agreement on the recognition of the Russian or Ukrainian Unified Exam has not been reached.
So, you need to prepare to take Selectividad. And pass it with an average score of at least 4.5. And although, as of June 7, 2014, international students may be exempt from the PAU (University Access Test) exam, many universities have reserved the right to require the Selectividad.
What kind of exam this is, how to prepare for it and how to calculate your overall score will be discussed in detail in a separate article. Now we just note that this exam consists of two parts: Mandatory phase and Voluntary.
In fact, it is not entirely voluntary, of course, but very necessary if you want to score more points for admission. And the choice of available faculties and specialties depends on what compulsory and additional disciplines the future student chooses.
Is it possible to study at a Spanish university in English or Russian?
To the great regret of Russian-speaking applicants, it is impossible to study or take exams in Russian at universities in Spain. Teaching takes place in Spanish, sometimes not all disciplines are taught in English, and quite a few subjects are taught in the second official language of the autonomy.
What does it mean? That, for example, in Barcelona some of the compulsory subjects will be taught in Catalan, in Valencia - in Valencian, in Santiago de Compostella - in Galician, in Bilbao - in Euskera (Basque language).
Entrance exams
In addition to homologating the certificate and passing the Seltctividad, it is likely that you will have to take entrance exams. Each public and private university in Spain independently determines which and how many additional exams an applicant must take to enter a certain specialty of this particular educational institution. And in what languages.
In addition, this question is revised every year, depending on the popularity of the faculty. Therefore, up-to-date information must be requested from the university dean’s office.
If you are a second year student or higher
If you are already studying at a university in your country and want to continue your education in Spain, you have the opportunity to transfer to a public university in Spain. Whether you can do this or not depends on several factors: whether you know Spanish at a sufficient level to study and whether the host University in the Kingdom of Spain has free student exchange places.
You must also show and the host Spanish university confirm and recognize at least 30 completed academic credits. How to do this and how to document it should be found out at your university. But to the dean’s office of a university in Spain, you need to provide, in addition to your passport and Foreigner Identification Number (NIE), the following documents:
- Academic certificate of completion of the course
- Certificate of grades indicating the minimum score for passing the subject
- Number of hours in each discipline (per year, per semester)
- Program for each discipline
- Syllabus
All these documents must be apostilled by the Ministry of Education of your country and translated into Spanish by an accredited translator.
If you are a university graduate with a higher education diploma
This option is intended for those who have already graduated from university and wish to enroll in a master's program to complete their education in Spain, and ultimately receive a diploma from a Spanish university and a master's degree. Everything is a little simpler here. It is enough to confirm your higher education diploma with the Ministry of Education and Vocational Training of Spain and apply for admission to the desired University of Spain for the Master program.
And, of course, to speak Spanish or English, if the University allows it, sufficiently, this is level C1, to write a dissertation and freely use scientific sources.
Features of training
Higher education institutions in Spain enjoy a special reputation among European students. Most boast an ancient history, the highest quality standards and a special democratic atmosphere. In addition to the prestige of local universities, applicants are attracted by a number of advantages:
- Large selection of establishments (including 50 public and 32 private).
- Centuries-old academic traditions combined with modern equipment.
- Highly qualified teaching staff (specialties such as history, geography, Latin, philosophy, and physics are especially famous).
- The National Institute annually checks the quality of teaching at all levels, from primary to higher education.
- Entrance exams take place from the end of June to September.
- Studying is distinguished by a credit system, in which there is a minimum of credits (points) required for transfer to the next course; the cost of loans for residents and non-residents is different.
- The most comfortable conditions: several options for distance courses are offered, all kinds of student benefits and discounts, access to an extensive library collection and lectures by world-famous professors.
In addition, the following advantages are most often decisive for applicants:
- Small groups, individual approach.
- Professional focus from day one.
- The cost of training is lower than in many countries of the world, while the diploma is highly rated internationally.
- Favorable climate for the development of entrepreneurship.
- Immersion in a unique cultural environment, acquaintance with the history and architecture of the Kingdom, the advantages of a mild climate and Mediterranean food.
How to enter a university and get an education in Spain
For those who intend to gnaw on the granite of science in the land of Cervantes, there are three main ways to realize their dreams, depending on the preparation and status of the student. Let's look at each of them.
We enter after school
Admission depends on whether you completed school directly in the Kingdom or in another country. The first case assumes that the student has a residence permit and a certificate in Spanish, which eliminates the need for document homologation. In the second situation, the applicant will need to have sufficiently good language skills to study, as well as translation and certification of the documents listed above.
Transferring from a Russian institution
Students of our national alma mater have the opportunity to transfer. The list of necessary actions in this case includes passing an exam confirming the level of the Spanish language, and, possibly, passing a number of disciplines. Some universities carry out transfers with some rollback - for example, by one course. Also, many Russian institutions offer to study for six months or a year at universities in the Kingdom on exchange, which can be an excellent way to get acquainted with the educational process and the country.
We are applying for a master's degree
The main requirements for applicants to “master” programs are a bachelor’s degree and language proficiency (minimum B2). However, more and more schools offer to study in English, while simultaneously “pushing up” Spanish in intensive classes. Admission to a master's program is usually carried out on a competitive basis; the average score from the bachelor's certificate is taken as the basis. Homologation and passing entrance exams are not required in this case.
Language of instruction in Spanish universities
Obtaining higher education in Spain is prestigious and profitable.
Education at public universities in Spain is conducted in Spanish, but you can also choose an English-language program. Also, depending on the region, the program additionally studies the language of the autonomous community in which the university is located. To enroll in a bachelor's degree, you do not need to prove your knowledge of Spanish, because the Spanish language exam will be included in the entrance exams.
To enroll in a Spanish university for a master's degree, you will need to confirm your level of Spanish language proficiency. To do this, you need to obtain a certificate that confirms level B1-B2. Spanish universities accept DELE, SIELE, CCEE certificates.
A significant advantage is that in Spain you can enroll in an English-language program, then you need to confirm your English proficiency at level B1.
How much does it cost to study for a higher education program at a university in Spain?
The specificity of the Spanish educational process lies in the payment procedure: skills are taken into account in points (creditos). These are unique points that can be collected for attending lectures, submitting papers, defending a dissertation or a thesis: one “credit” is equal to 10 hours of classes. The amount of “credits” accumulated is used to judge the student’s degree of preparation and achievements. So, for a bachelor's degree you need at least 240 for all 4 years, for a master's degree - from 60 to 120. You are allowed to attend more classes or areas, but each student is required to complete the credit minimum to receive a diploma.
The price of one item varies and depends on the prestige of the institution and the complexity of the specialty. So, studying for a bachelor's degree at Universidad Autonoma de Madrid, you will have to pay from 20 to 30 euros for each credit, i.e. about 1200 euros per year. The most expensive are the scientific specialties that require large expenses from the university: medicine, chemistry, biomedicine, etc. In addition, being a poor student is not only troublesome, but also expensive: to repeat a loan if you fail, you will have to pay a tidy sum, sometimes double the amount.
Obtaining higher education in Spain for Russians
Prices in public educational institutions are set by the government of each autonomous community and can vary quite widely. For example, future doctors studying the basics of medicine at a public university in Andalusia pay 800 € per year, while their “colleagues” in Catalonia pay about 2,500 €.
Prices for students from countries outside the European Union and non-residents also usually differ from those used by Europeans, sometimes quite significantly. At the same Universidad Autonoma de Madrid, the price of study for non-resident students increases to 120 euros per credit, so the annual course will cost them 7,200 euros. Thus, if the applicant has a resident card, it is necessary to provide it to the admissions committee before enrollment - then payment will be made according to the standard price list intended for residents and Spaniards. The country also has a developed system of discounts and bonuses, which are provided to successful students by academic exchange services and other international funds. By resorting to them, you can reduce your study costs by up to 50%.
Autonomous University of Madrid
Founded in 1968, the Autonomous University of Madrid is currently ranked 159th in the 2021 QS World University Rankings, and is also ranked among the top 50 universities under 50 years of age. It has over 36,000 students across eight faculties and is particularly famous for its Faculty of Law. It has three campuses, the main one, Campus Cantoblanco, located 15 km north of Madrid. The Autonomous University of Madrid is proud to be the alma mater of His Majesty King Felipe VI of Spain.
Grants and scholarships
They are offered by most European educational centers, including the most prestigious ones, however, they are quite difficult to obtain: competition for a place can range from 20 to 50 people. It is also important to carefully study the conditions for providing assistance: some programs require staying in your home country 50% of the time, others provide fines for failure to comply with requirements. Sometimes it is more rational to apply to study at an inexpensive institute in a small town, where the annual fee does not exceed 700 euros.
If you still decide to take a risk and try your luck, you will have to take the following steps:
- Select a suitable scholarship program on the websites of relevant educational foundations and organizations.
- After being enrolled in the list of university students, apply for financial support.
- Collect and send the package of documents requested on the same website: prepare a detailed resume, letters of recommendation and motivation, and pass testing.
Student expenses
In addition to tuition fees, administrative fees, insurance, diploma defense are additionally paid - only about 500-700 € per year. Be prepared to also include items in your budget such as:
- Textbooks, manuals, office.
- Accommodation in a student residence or renting an apartment (from 400 euros per month).
- Transport, food, clothing, entertainment (from 300-500 euros per month, but it all depends on the person’s lifestyle, needs, etc.).
Living expenses
- To rent an apartment. In the capital, the cost of a small studio apartment varies from 400 to 1200 euros per month; in the provinces it is about a third cheaper. The advantage of this option is that you choose comfortable housing, the disadvantage is the cost of transportation.
- The cost of a student dormitory is approximately 300 euros/month. It varies depending on the number of students living in one room and the availability of various amenities. There are dorm rooms, which are mini-apartments, with an individual bathroom and kitchen. In other cases, there may be one bathroom for several student rooms. Residence halls are usually located on college campuses and there are no transportation costs.
- Transport costs: monthly subscription for all types of transport - 50 euros.
- Nutrition. 100-200 euros.
List of the most prestigious universities in Spain
Among the most popular institutions among foreign applicants are both private and public centers. Each of them has a unique history and an interesting set of specialties, but the following training centers appear most often in international rankings:
- Universitat de Barcelona
- Universitat Pompeu Fabra
- Universitat Autonoma de Barcelona
- Universitat Politecnica de Catalunya
- Universidad Autonoma de Madrid
- Universidad Politecnica de Madrid
- Universidad de Valencia
- Universidad de Granada
- Universidad Complutense de Madrid
- Universidad de Santiago de Compostela
- Universidad de Navarra
In the article, we told how Russians can enroll in a Spanish university immediately after school and what to do in order to get into school as an adult. Barcelona Realty Group specialists will be happy to assist in obtaining a student visa, selecting a school, and collecting a package of documents. You can always seek professional advice by sending a request to [email protected] or calling +7 (965) 404-45-55 (WhatsApp).
The best universities in Madrid
According to QS Best Student Cities 2015, Madrid is ranked second in the ranking of Spanish cities and 39th in the world. The capital of Spain is the largest city in the kingdom, as well as Europe's largest financial, cultural and administrative center.
Autonomous University of Madrid – Universidad Autónoma de Madrid:
- one of the best public universities in the country. Founded in 1968 at the same time as the Autonomous University of Barcelona. Throughout its academic activities, it has been distinguished by high standards of educational quality;
- according to the QS World University Ranking, it is among the top 300 universities in the world, in the category of natural sciences it ranks 61st in the world, the Faculty of Mathematics is among the 75 best in the world;
- the Faculty of Law is considered one of the most prestigious in Spain;
- according to Thomson Reuters, researchers from this university were cited most often in scientific publications in 2011;
- features extremely active student communities.
Madrid Complutense University - Universidad Complutense de Madrid:
- one of the largest and oldest universities in Spain, founded in 1499;
- among the university's graduates are world-famous cultural figures: Miguel de Cervantes, Francisco Quevedo, Tirso de Molina, Calderon de la Barca, Lope de Vega, as well as seven Nobel laureates, members of the European Commission, presidents of the European Parliament, NATO Secretary General, UNESCO Director General and other famous People;
- Currently, more than 86,000 students are studying at the university;
- according to the influential Spanish newspaper El Mundo, the university is rightfully considered the most prestigious educational institution in Spain.
University of Madrid Carlos III - Universidad Carlos III de Madrid:
- a relatively young, actively developing state university, founded in 1989;
- the university is named after King Carlos III of Spain, and this fact obliges us to be the best of the best;
- the Faculty of Economics is ranked in the top 50 in the world, and the study programs in business administration, economics and law are considered the best in the country;
- According to the QS ranking, it ranks 142nd in Europe.
King Juan Carlos University – Universidad Rey Juan Carlos:
- one of the best young public universities in Madrid, opened in 1996;
- has four modern campuses;
- offers a wide range of programs: 64 bachelor's degree programs, 44 double bachelor's degree programs, 81 master's degree programs.
Madrid Polytechnic University – Universidad Politécnica de Madrid:
- state university, opened in 1971. Most of the university's schools and centers were still active in the 18th and 19th centuries;
- according to the annual ranking of the El Mundo newspaper, the university is the best technical university in Spain;
- most of the university's engineering schools are the best not only in Spain, but also in Europe;
- The university offers a huge selection of double diplomas issued jointly with leading universities in the world.